From September 22 to 25, 2025, the 23rd session of the Working Party on Automated/Autonomous and Connected Vehicles (GRVA) under the UN World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations (WP.29) was held in Geneva, Switzerland. Associate Research Fellow WANG Hong from the team of Academician LI Jun at Tsinghua University's School of Vehicle and Mobility attended the meeting as a member of the Chinese delegation. She presented and exchanged views with participating experts on the "SOTIF Index-Based Driving Safety Evaluation Method for Automated Driving Systems (ADS)."

The meeting brought together over 100 experts from contracting party governments including China, Germany, Japan, the United States, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, the Netherlands, Russia, Canada, South Korea, and the European Union (EU), as well as from international and industry organizations such as the International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (OICA), the European Association of Automotive Suppliers (CLEPA), and SAE International. The session was chaired by GRVA Chair Richard Damm. The Chinese delegation was led by Vice-Chair of GRVA, CHEN Chunmei, First-Level Inspector from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology's Department of Equipment Industry I, and included experts from China Automotive Technology and Research Center Co., Ltd., Tsinghua University, the Research Center for Road Traffic Safety of the Ministry of Public Security, and the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, among other institutions.

Since the establishment of the Safety of the Intended Functionality (SOTIF) Working Group under the Intelligent and Connected Vehicles Industry Innovation Alliance on May 29, 2020, Academician LI Jun's team has collaborated with over 80 domestic organizations to develop the SOTIF index framework, engaging in extensive exchanges and discussions with experts both in China and internationally. During this GRVA session, this research outcome was presented as a formal proposal. Dr. WANG Hong provided a comprehensive introduction to the "SOTIF Index-Based Driving Safety Evaluation Method for ADS."
This method draws inspiration from the successful paradigm of vehicle pollutant emission control over the past three decades: 1) The evolution from Euro 1 to Euro 7 standards, involving the quantification of pollutant emission metrics and the gradual reduction of emission limits towards near-zero emissions; 2) The definition of emission test cycles representing real-world driving conditions, ultimately leading to real driving emission (RDE) tests; 3) The continuous development of advanced vehicle emission testing equipment to ensure the authenticity and reliability of measurement results.
Building on this paradigm, the team's proposed safety evaluation method for automated driving corresponds to three core components. Firstly, the "SOTIF Index-Based Driving Safety Evaluation Method for ADS" proposes using the SOTIF Index to characterize the conversion rate of known unsafe scenarios and the credibility of validating unknown unsafe scenarios. Through the progression from SOTIF Index 1.0 to 2.0 to X.0—analogous to the evolution from Euro 1 to Euro 7 in emission control—the method aims to gradually reduce the unknown unsafe scenarios for ADS, "cut off" the long-tail effect, ultimately realizing the safety vision of near-zero accidents for ADS.
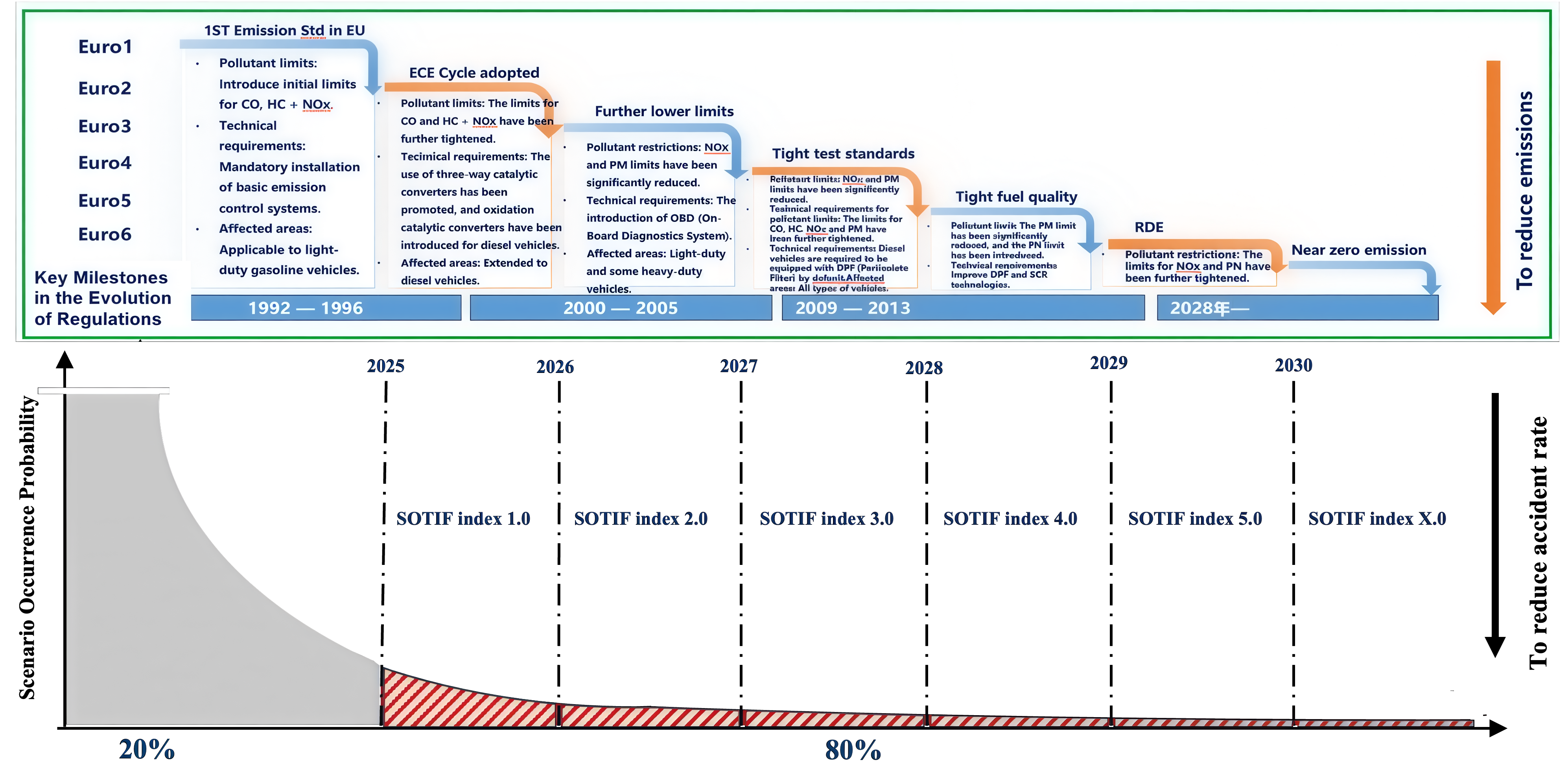
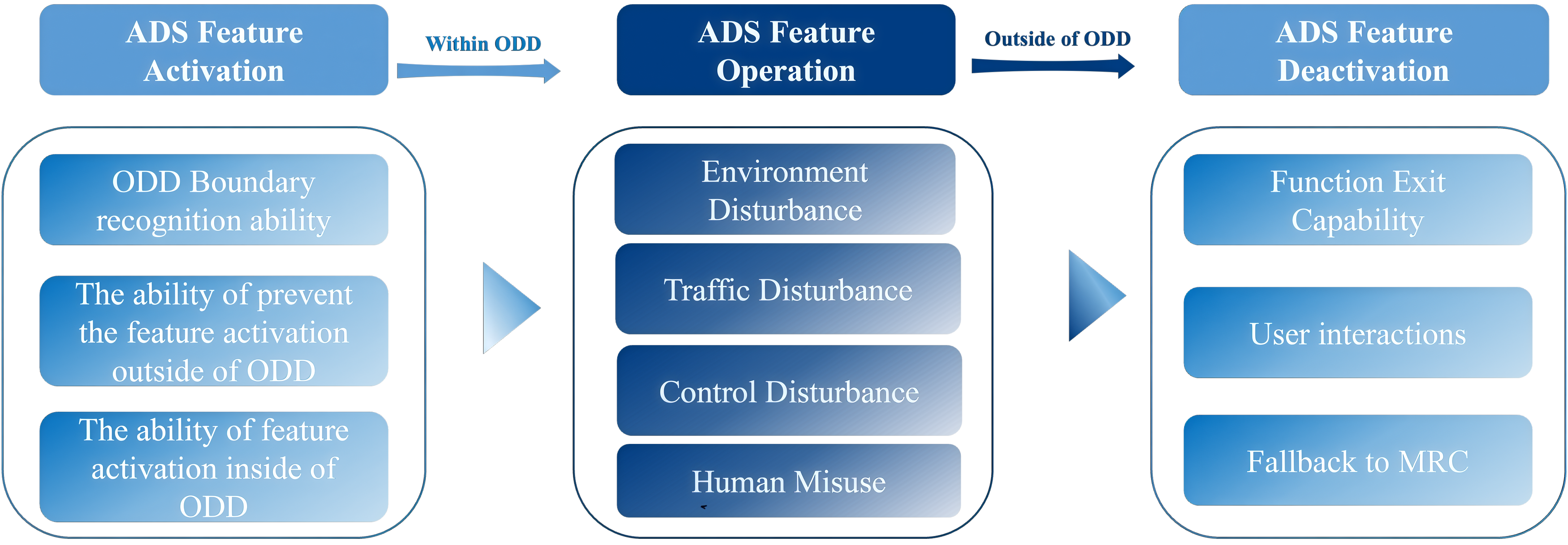
Secondly, analogous to the driving cycles for emission testing, the "SOTIF Index-Based Driving Safety Evaluation Method for ADS," guided by the Operational Design Domain (ODD) definition framework, defines a full-process test and evaluation scenario covering function activation, operation, and deactivation. Currently, 100 test scenario categories for SOTIF Index 1.0 have been completed.
Finally, mirroring the advanced equipment for emission testing, the "SOTIF Index-Based Driving Safety Evaluation Method for ADS" establishes a vehicle-in-the-loop (VIL) testing environmental laboratory that simulates real weather conditions, road structures, and traffic flow, ensuring efficient and credible testing of ADS driving safety. The presentation also introduced the AI-SAP testing method and multi-vehicle test results based on the SOTIF index framework, developed in collaboration with domestic testing institution China Merchants Vehicle Testing & Research Institute (Chongqing).
The "SOTIF Index-Based Driving Safety Evaluation Method for ADS" attracted significant attention from various parties present, including France, Canada, Germany, and SAE International from the United States. During the meeting, the Chinese representatives actively addressed questions from foreign experts, enhancing international understanding of China's SOTIF testing approach and fostering exchanges on automated driving safety evaluation methods. Moving forward, Academician LI Jun's team from the School of Vehicle and Mobility at Tsinghua University will continue to participate deeply in the development of automated driving safety regulations within UN/WP.29. They will leverage their professional expertise in SOTIF research for automated driving, supporting the internationalization of China's intelligent and connected vehicle regulations and standards, and contributing Chinese expertise to promoting the safe and sustainable development of the global intelligent and connected vehicle industry.
